Introduction: The Growing Importance of Fish Feed Production
The global aquaculture industry has grown exponentially over the past decade. With increasing demand for high-quality protein and sustainable fish farming practices, more investors and farmers are looking to establish their own feed production lines.
Yet, despite its popularity, many newcomers struggle with one key question: how much should a fish feed production line cost, and what determines the price?
This guide dives deep into the pricing, production capacity, technology, and ROI of fish feed production lines, offering insights from real-world cases and our Fish Feed Production Line solutions.
Key Factors Influencing Fish Feed Production Line Costs
Before discussing specific price ranges, it is essential to understand the multiple variables affecting cost. Based on our global customer feedback and technical insights, nine main factors influence the final investment:
1. Production Capacity
The hourly output of a line significantly determines cost. Lines range from 100kg/h to 10 tons/h. Capacity affects motor power, gear strength, extruder barrel size, and automation complexity.
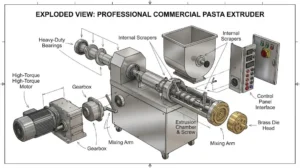
2. Type of Extruder
Dry Type: Lower cost, ideal for floating feed, simple structure
Wet Type: Higher cost, requires boiler, provides better gelatinization
Twin-Screw: Premium choice for high-grade feed, uniform extrusion, high durability
3. Automation Level
Manual / Semi-automatic: Suitable for small workshops
Fully Automatic PLC: Medium factories
Smart Factory Integration: Large-scale modern production
4. Materials & Build Quality
Barrel alloy and hardness
Motor brand and efficiency
Cutter system
Stainless steel components for corrosion resistance
5. Feed Type Requirement
Floating feed
Sinking feed
Slow-sinking feed
Different feed types require adjustments in extrusion temperature, moisture content, and starch gelatinization.
6. Local Power Standards
Voltage, frequency, and availability of three-phase power affect motor selection and cost.
7. Installation Conditions
Factory space
Foundation strength
Ventilation and climate considerations
8. After-Sales Service & Spare Parts
Long-term maintenance costs often outweigh initial investment. Reliable after-sales support reduces downtime.
9. Brand & Technology
European brands are usually 3–10× more expensive than Chinese manufacturers but may offer advanced automation or energy-saving technology.
Detailed Price Ranges: Small, Medium, Large
Small Fish Feed Production Line (100–300 kg/h)
Typical Price: USD 8,000 – 25,000
Suitable for small farms, startups, and local workshops
Configuration: Crusher → Mixer → Fish Food Extruder (dry type) → Dryer → Seasoning → Packing

Medium Fish Feed Production Line (300–1,000 kg/h)
Typical Price: USD 25,000 – 80,000
Used by medium feed factories, government projects, expanding aquaculture businesses
Configuration: Double-shaft mixer → Screw feeder → Food Fish Processing Equipment (dry/wet) → Multi-layer dryer → Coating → Semi-auto packing

Large Fish Feed Production Line (1–10 T/H)
Typical Price: USD 80,000 – 650,000
Target: Large feed factories, exporters, national aquaculture corporations
Configuration: Twin-screw Fish Food Processing Machine, PLC automation, steam conditioning, energy-saving dryers, stainless steel structure

Why Prices Vary: Understanding Technical Differences
Dry Extruder: Cheapest, basic floating feed
Wet Extruder: Medium cost, better gelatinization, high stability
Twin-Screw Extruder: Premium, high-grade feed, uniform output, long service life
Other factors: motor brand, steel quality, coating system, automation level, spare parts availability.
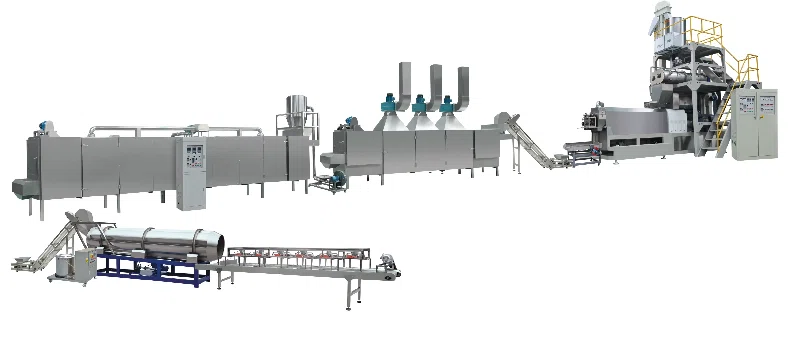
Production Flow Diagram & Detailed Process
1. Raw Material Grinding
Pulverizes corn, soybean, wheat, fish meal, etc.
Ensures uniform particle size for consistent extrusion
2. Mixing
Homogenizes protein, starch, fat, vitamins
Reduces uneven feeding to extruder
3. Extrusion
Raises temperature for starch gelatinization
Shapes pellets, adjusts density for floating or sinking feed
4. Drying
Reduces moisture to 10–12%
Preserves nutrients and prolongs shelf life
5. Coating & Flavoring
Adds fish oil, attractants, micronutrients
Improves feed palatability
6. Cooling
Lowers pellet temperature
Prevents condensation during storage
7. Packing
Automatic or semi-auto packing
Ensures consistent weight and hygienic packaging
Global Market Insights (2025 Data)
| Region | Popular Line Size | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Africa | 150–500kg/h | Tilapia farming |
| SE Asia | 1–3T/H | Shrimp & catfish industry |
| Middle East | 2–5T/H | Large feed distributors |
| S. America | 500–1000kg/h | Regional fish feed suppliers |
Investment & ROI Analysis
Small Line: 200kg/h → 1.5 tons/day → $60–120 profit/ton → Payback 1–3 months
Medium Line: 500kg/h → 4–6 tons/day → $70–150 profit/ton → Payback 2–5 months
Large Line: 2T/H → 16–40 tons/day → Payback 3–8 months
Key factors: raw material cost, labor, electricity, local market price.
Operating Costs Breakdown
Electricity consumption (5–20 kWh/ton depending on line)
Labor (2–12 workers depending on automation)
Raw material (50–70% of total cost)
Maintenance & spare parts (1–5% of investment annually)
Packaging & logistics

Advanced Tips to Reduce Cost & Improve Quality
Use high-quality raw material
Optimize extruder temperature and moisture
Maintain barrel & screw regularly
Implement automated batching
Reuse cooling water & energy-saving dryer
Why Choose Our Fish Feed Production Line
Capacity flexibility (100kg/h–10T/H)
15+ years design experience
Global installation & after-sales support
Energy-saving and cost-effective solutions
One-stop turnkey projects
Extended FAQ (Q&A Section)
-
Q1: Can I upgrade a small line to medium later?
Yes, all our lines are modular and upgradable.
-
Q2: How to choose floating vs sinking feed extruder?
Depends on fish type: surface feeders → floating; bottom feeders → sinking.
-
Q3: How often should maintenance be done?
Daily: clean screw & barrel;
Monthly: check motor & bearings;
Yearly: overhaul key parts. -
Q4: Is on-site installation worldwide available?
Yes, professional engineers can assist globally.
-
Q5: What is the expected service life of extruder?
High-quality extruder: 10–15 years with proper maintenance.
-
Q6: How to reduce energy cost?
Use energy-saving motors
Recover heat from dryer
Optimize process parameters