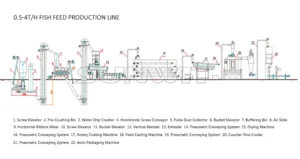
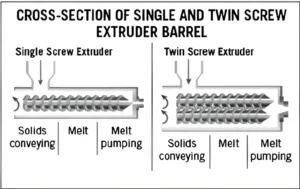
What is the fish feed extruder machine in aquatic food pellet production?
Interesting posts
- Starting a Pasta Business: The 2025 Equipment Guide
- Alternative Protein Sources for Fish Feed: A Practical Guide
- Ultimate Buyer’s Guide 2025: What Is the Typical Price Range for a Small, Medium, and Large Fish Feed Production Line?
- Single-Screw vs Twin-Screw Food Extruders: A Complete Guide for Modern Food Manufacturers
- What is the Difference Between Floating and Slow-Sinking/Extruded Pellets?
- What Raw Ingredients Are Commonly Used in Fish Feed?
- Complete Guide to Fish Feed Production Line: From Raw Materials to High-Quality Pellets
- What is the Difference Between a Fish Feed Extruder and a Pellet Mill?

Aquaculture has evolved significantly over the past few decades, with an ever-growing emphasis on efficiency, sustainability, and the nutritional quality of fish feed. In the heart of this evolution is the cutting-edge technology of the fish feed extruder machine, which plays a crucial role in producing high-quality aquatic food pellets. This guide provides a comprehensive exploration of the fish feed extruder machine, offering insights into the entire process – from raw material preparation to finished feed pellets – and discussing its benefits over traditional pelleting methods.
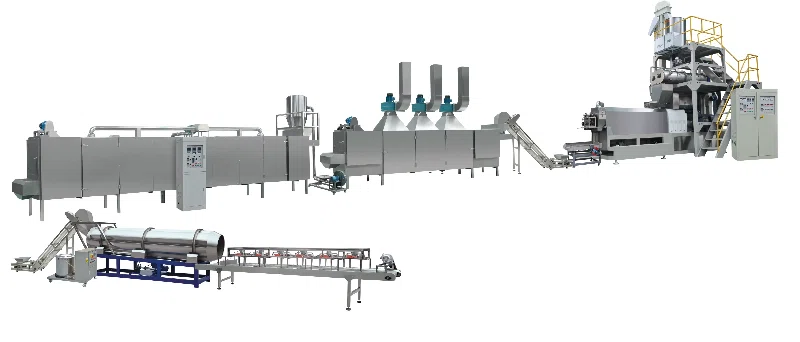
An Overview of Aquatic Food Pellet Production
With the increasing demand for high-nutrition fish feed and more effective aquaculture practices, producers worldwide are rapidly adopting advanced technologies. One of these technologies is the extrusion process used to form aquatic food pellets. Unlike conventional pellet mills, fish feed extruder machines rely on high temperature, high pressure, and mechanical force to transform raw materials into nutrient-rich, porous pellets. This not only enhances digestibility but also significantly improves nutrient absorption.
The production process is tailored to meet specific nutritional needs based on the species and feeding habits of fish. For instance, some fish species benefit more from floating pellets, while others thrive on sinking or slow-sinking pellets. By utilizing advanced extrusion techniques, producers can optimize pellet characteristics such as buoyancy and stability, leading to improved feed conversion rates and overall fish growth.
The Role and Technology Behind the Fish Feed Extruder Machine
The fish feed extruder machine is a sophisticated piece of equipment designed to process a variety of raw materials into uniform, high-quality aquatic food pellets. At its core, the extruder forces a precisely ground and mixed feed blend through a specially designed die. During this process, the combined action of heat, pressure, and mechanical force induces starch gelatinization, causing the pellets to expand and develop a porous structure. This results in pellets that are not only easy for fish to digest but also retain essential nutrients.
Furthermore, this extrusion process circumvents the need for a steam boiler, distinguishing it from traditional pelleting machines. Producers find that the extruded pellets have a lower bulk density, making them ideal for producing floating pellets that fish can easily locate and consume. This is particularly beneficial for species that feed on the water's surface.
One of the key advantages is that the extruder allows for precise control over the pellet properties. For example, by adjusting the temperature, moisture, and pressure parameters, manufacturers can control the buoyancy of the pellets. This versatility makes the fish feed extruder machine an indispensable tool in modern aquaculture.
The Comprehensive Production Process
A successful aquatic food pellet production involves multiple well-synchronized stages. Each stage contributes to the overall efficiency and quality of the final feed product. Here, we detail the key steps of the production process:
Raw Material Preparation
The process starts with the careful selection and preparation of raw materials. Essential ingredients typically include fishmeal, soybean meal, wheat flour, fish oil, vitamins, and minerals. These components are weighed and mixed in specific proportions to ensure that the resulting pellets offer a balanced diet for the fish.
Grinding and Mixing
Once the raw materials are prepared, they undergo a grinding process to ensure a uniform particle size. This step is critical, as it enhances the digestibility of the pellets by facilitating the breakdown of ingredients during extrusion. After grinding, the mixture is thoroughly blended using advanced feed mixers, ensuring that every pellet contains a homogenous distribution of nutrients.
Pelletizing and Extrusion
At the heart of the process is the pelletizing stage. Here, the mixed feed is introduced into the fish feed extruder machine. During the extrusion phase, the feed mixture is subjected to high temperature and pressure, which activates the starch gelatinization process. This not only enhances the digestibility but also imparts a porous texture to the pellets. Following extrusion, the continuous feed is cut into uniform pellets and further processed.
During the pelletizing phase, particular care is taken in controlling parameters such as moisture, temperature, and pressure to achieve the desired pellet characteristics. In this way, the extruder can generate pellets suited for various feeding strategies, ranging from floating to slow-sinking forms.
Drying and Cooling
Following pellet formation, the next crucial step is drying and cooling. Reducing the moisture content is vital for both the stability and shelf life of the feed pellets. Specialized dryers and cooling systems are employed to ensure the pellets reach an optimal moisture level without compromising their nutritional value.
The entire production line is meticulously engineered to maintain the integrity of heat-sensitive nutrients, ensuring that the final product meets the stringent requirements of modern aquaculture.
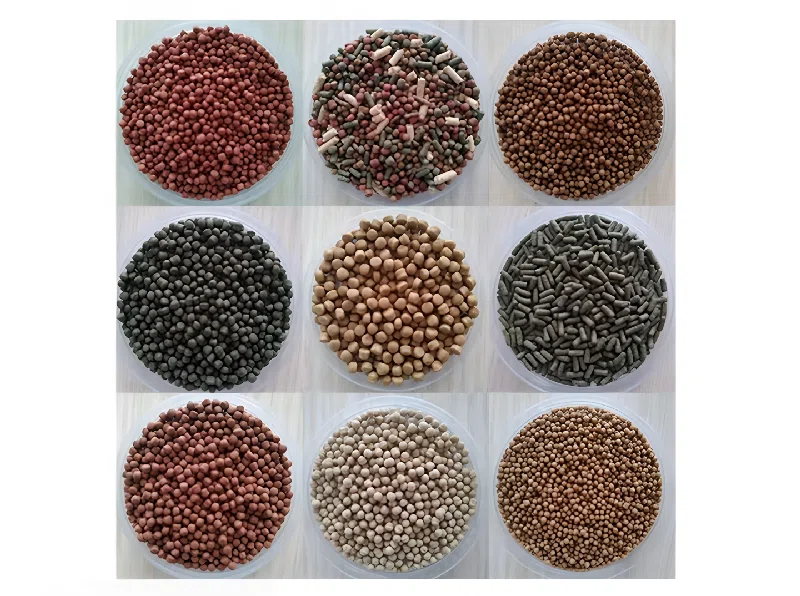
Types of Fish Feed Pellets and Their Specific Applications
Aquatic food pellet production has evolved to address the diverse feeding behaviors of different fish species. The primary classifications include:
Floating Fish Feed Pellets
Designed primarily for species like tilapia and carp that feed near the water surface, floating pellets remain easily visible, thereby minimizing waste. The extrusion process, through controlled expansion and density management, ensures that these pellets maintain buoyancy for extended periods, giving fish ample time to locate and consume them.
Sinking Fish Feed Pellets
In contrast, sinking pellets are intended for bottom-dwelling fish such as catfish. These pellets rapidly descend to the substrate, reducing the risk of food competition and waste accumulation. By matching the pellet properties with the fish’s feeding habits, aquaculture operations can maximize feed efficiency.
Slow-Sinking Fish Feed Pellets
A middle ground between floating and sinking variants, slow-sinking pellets are engineered to gradually descend through the water column. They cater to species that feed in mid-water zones, such as rainbow trout and salmon, and provide a balanced approach to nutrient delivery across different water layers.
These diverse pellet types are created through minor adjustments in the extrusion and cutting process, emphasizing the flexibility of modern fish feed extruder machines.
Advantages of the Extrusion Process in Fish Feed Production
Extrusion technology offers numerous benefits that distinguish it from conventional pelleting methods. Some of the key advantages include:
- Fish Food Extruder: The extrusion process allows for the production of feed pellets with controlled buoyancy, making it possible to produce both floating and slow-sinking feed types based on specific dietary needs.
- Fish Food Processing Machine: Extruded pellets have enhanced nutrient availability, higher digestibility, and improved physical integrity compared to those produced by traditional pellet mills.
- Food Fish Processing Equipment: The controlled extrusion process minimizes the loss of heat-sensitive nutrients by optimally managing temperature and moisture, thereby preserving the nutritional quality of the feed.
- Better feed palatability and flavor, which directly influence the feeding behavior and overall growth performance of fish.
- Reduced fines and dust production, resulting in cleaner production facilities and more efficient feed utilization.
Moreover, the extrusion process provides economic advantages. While the initial capital investment in extrusion equipment may be higher, the long-term benefits include reduced raw material waste, improved feed efficiency, and lower overall production costs.
The Equipment Behind High-Quality Pellet Production
In modern aquaculture, selecting the right equipment is essential to produce consistent, high-quality feed pellets. The food Extruder Machine stands at the forefront of this technology. It is specially designed to handle a variety of feed ingredients, ensuring optimal processing conditions throughout each stage of pellet production.
Manufacturers have invested heavily in machinery that can adapt to different production scales—from small-scale operations to large industrial facilities. Alongside the extruder machine, modern production lines integrate grinders, mixers, dryers, coolers, and packaging machines to create a seamless production process that minimizes downtime and maximizes efficiency.
The continuous innovations in equipment design have also led to improved automation and process control. This evolution not only boosts productivity but also enables manufacturers to tailor feed formulations to meet the evolving nutritional needs of different fish species.
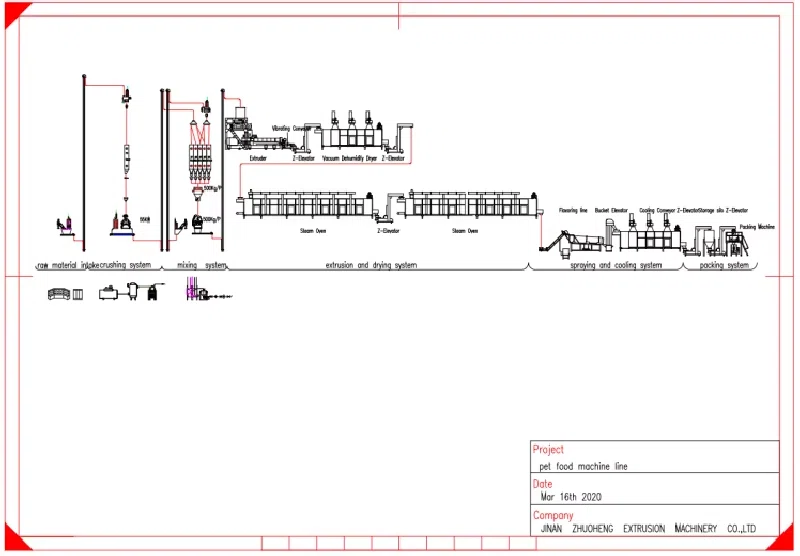
Comparing Extruder Machines and Traditional Pellet Mills
A common question among those entering the field of aquatic feed production is the difference between extruder machines and conventional pellet mills. While both approaches aim to transform raw feed ingredients into uniform pellets, the methods differ significantly.
Traditional pellet mills compress and mold the feed mixture into pellets, generally without the benefits that extrusion technology provides. In contrast, extruder machines use a high-pressure, high-temperature process that not only forms the pellet but also enhances its nutritional profile by improving starch gelatinization and nutrient availability.
One clear advantage of using the extrusion method is its ability to control the buoyancy of the final product. For example, extruded pellets can be engineered to float, which is ideal for species that feed near the surface, or they can be adjusted to slow-sink or sink quickly, meeting the specific dietary needs of bottom feeders.
The higher capital expenditure required for an extrusion system is offset by the improved feed quality and the efficiency gains in the production process. The resulting pellets tend to have better integrity, reduced fines, and overall superior performance in fish feeding trials.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
The global aquaculture industry continues to grow, driven by the increasing demand for seafood and the need to produce high-quality feed that optimizes fish growth and health. As technology advances, the adoption of extrusion systems in feed production is likely to increase, supported by several market trends:
- Rising consumer demand for sustainably produced seafood.
- The increasing use of automation in feed production lines.
- The development of customized feed formulations tailored to specific species and environments.
- The growing emphasis on reducing waste and improving feed conversion ratios.
Leading manufacturers are continuously refining extrusion techniques to cope with these dynamic market requirements. The integration of advanced process controls, real-time monitoring, and energy-efficient drying systems is setting new benchmarks in the industry. Over time, innovations such as smart sensors and predictive maintenance will further streamline operations, ensuring that aquaculture facilities can scale production without sacrificing feed quality.
In this context, the role of the fish feed extruder machine becomes ever more critical. By leveraging the advantages of extrusion technology, producers can stay ahead of the curve, meeting evolving nutritional standards and catering to the specific needs of diverse aquatic species.
Technological Innovations and Process Optimization
The world of aquatic feed production is in a state of continuous evolution, with technological breakthroughs paving the way for process optimization. Recent innovations in extrusion technology focus on achieving even higher levels of feed digestibility and nutritional value. Manufacturers are now able to fine-tune process parameters such as moisture content, temperature, and pressure with unprecedented precision.
These innovations have enabled the production of feed pellets with targeted physical and nutritional characteristics. By doing so, producers can formulate specialized feeds that not only meet the basic dietary needs of fish but also boost their immune responses and overall growth rates.
Additionally, the integration of advanced automation into the production line minimizes human error and ensures consistency in each batch. This is particularly valuable when scaling up operations, as it guarantees that every pellet meets the high standards required in modern aquaculture.
In practice, continuous improvements in equipment design – from the initial raw material preparation to the final packaging stages – enable producers to achieve remarkable results. Quality control measures such as in-line moisture sensors and pellet integrity testers help detect and correct deviations in real time, ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications.
Strategies for Cost-Effective Production
Despite the technological complexity and high initial investment associated with extrusion equipment, many producers find that the long-term benefits justify the expenditure. Key strategies for cost-effective production include optimizing raw material usage, implementing energy-efficient drying and cooling systems, and utilizing automated process controls to maintain consistent pellet quality.
Regular preventive maintenance is also essential. By scaling production gradually based on market demand and maintaining a rigorous maintenance schedule, operations can minimize downtime and improve overall cost-efficiency.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
In today’s environmentally conscious market, sustainability is a critical factor influencing production methods. The extrusion process, with its capacity for precise control and efficient use of raw materials, offers several environmental advantages. By minimizing waste during production and enhancing feed conversion rates, extruded pellets contribute to a lower environmental footprint.
Sustainable practices in feed production not only preserve natural resources but also help aquaculture operations adhere to increasingly strict environmental regulations. This aligns with global trends toward sustainable seafood production and responsible aquaculture practices.
Many modern fish feed extruder machines are designed with energy efficiency in mind. Innovations in drying and cooling systems help reduce energy consumption significantly, thereby lowering the overall environmental impact of the production process.
Sustainability is further enhanced by advancements in raw material sourcing. The industry increasingly relies on renewable, high-quality ingredients that support the well-being of aquatic species, ensuring that aquaculture continues to evolve as a sustainable and responsible food production sector.
Optimizing Production with Process Integration
In today’s competitive aquaculture market, integrating multiple production processes into a streamlined system is essential. By connecting every stage—from raw material preparation to packaging—a cohesive production line is achieved that minimizes downtime and maintains consistent quality.
Automated monitoring systems and process sensors enable manufacturers to track every stage in real time. Any deviations are quickly identified, allowing for rapid adjustments that maintain process consistency and optimize the nutritional content and physical properties of the feed pellets.
Integrating a high-quality fish feed extruder machine into a larger production line not only enhances product quality but also supports overall operational efficiency, ensuring that producers can meet rising market demands reliably and sustainably.
Innovations in Packaging and Distribution
Once high-quality fish feed pellets are produced, effective packaging and distribution become essential to maintain freshness and nutritional value. Modern packaging solutions, including vacuum sealing and moisture-resistant materials, protect the pellets during transit while also enhancing brand appeal.
Eye-catching, informative packaging that includes nutritional information and usage instructions helps build customer trust and brand recognition. The seamless integration of production, packaging, and distribution strengthens the reputation of producers as providers of premium-quality feed.
Case Studies and Industry Success Stories
Numerous aquaculture operations worldwide have successfully implemented extrusion technology to revolutionize their feed production processes. One notable success story involves a mid-sized aquaculture farm that transitioned from traditional pellet mills to an extrusion-based system, resulting in significant improvements in feed conversion ratios, reduced wastage, and enhanced overall fish growth.
Other implementations have focused on creating specialized feeds tailored to the unique requirements of local fish species. By optimizing production parameters such as moisture, temperature, and pressure, these producers achieved customized pellet buoyancy and texture, resulting in improved feeding efficiency and higher yields.
The integration of robust quality control measures and advanced production automation has led to reduced downtime, lower operational costs, and increased profitability for many producers who have embraced extrusion technology.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Although the benefits of extrusion technology are significant, challenges such as high initial capital costs and managing raw material variability remain. Manufacturers have addressed these issues by developing innovative process control strategies that maintain optimal conditions and by investing in routine maintenance and operator training.
These proactive measures help create a robust production process that delivers consistently high-quality aquatic food pellets while minimizing operational costs.
Conclusion: Future Prospects and Final Thoughts
The fish feed extruder machine has reshaped the landscape of aquatic food pellet production. With its ability to produce specialized pellets—whether floating, sinking, or slow-sinking—it offers aquaculture producers superior control over feed quality and process efficiency.
Looking ahead, the emphasis on sustainability, efficiency, and improved nutritional profiles will continue to drive innovation in extrusion technology. Investing in advanced equipment and integrating process automation is key to meeting future market demands.
Whether you are a seasoned aquaculture professional or new to feed production, embracing modern extrusion technology is a strategic move towards enhanced productivity and long-term success.
Q&A
Q1: What makes the fish feed extruder machine so effective in producing aquatic food pellets?
A: The machine uses high temperature, pressure, and mechanical force to gelatinize starch and create porous pellets. This process enhances nutrient availability, improves digestibility, and allows precise control over pellet buoyancy.
Q2: How do floating, sinking, and slow-sinking pellets differ in production and application?
A: Floating pellets are designed for surface feeders, sinking pellets are ideal for bottom feeders, and slow-sinking pellets offer a balanced option for mid-water feeders. These differences are achieved by adjusting extrusion parameters like moisture and density.
Q3: What are the main advantages of using extrusion technology over traditional pelleting methods?
A: Extrusion technology improves nutrient retention through controlled gelatinization, enhances pellet integrity and digestibility, and allows precise buoyancy control, resulting in superior feed quality with less waste.
Q4: Is the initial capital investment for extrusion equipment justified by the long-term benefits?
A: Yes. Although the upfront cost is higher, the long-term gains in feed quality, efficiency, and reduced waste contribute to significant overall cost savings.
Q5: How can I integrate a fish feed extruder machine into an existing production line?
A: Integration requires evaluating your current production setup, aligning raw material handling, and incorporating compatible equipment such as mixers, dryers, and packaging systems. Consulting with experienced manufacturers can help design a seamless production line.
Need Help?
Other questions need help