This whitepaper-level guide shows how pet food is manufactured — not just the step-by-step flow, but also compliance, supply chain, and market trends shaping investment decisions. Written for processors and B2B importers who need both technical clarity and business foresight.
Step-by-Step Process Overview
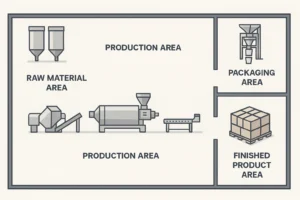
A robust process doesn’t start at the extruder; it starts with supplier approval and ingredient control. Below is a condensed map you can use as a quality baseline when auditing a partner or planning capacity.
Process flow diagram, clean infographic style: receiving → grinding → mixing → preconditioner → extruder → dryer → cooler → coater → packaging.

Steps (summary from table)
- Supplier approval & incoming checks – verify safety, composition, consistency.
- Grinding & sieving – achieve uniform particle size.
- Batching & mixing – ensure precise formulation.
- Hydration & preconditioning – hydrate starches before extrusion.
- Cooking & forming – “kill step” for pathogens, shaping via Pet Food Extruder.
- Drying – reduce moisture to prevent spoilage.
- Cooling – stabilize before coating/packaging.
- Coating – apply fats/flavors/preservatives.
- Packaging – ensure barrier and shelf life.
Dry vs. Wet vs. Semi-Moist — What Changes
Dry products rely on extrusion and drying, wet products rely on filling and retort sterilization, while semi-moist often use baking or molding. Moisture, packaging, and palatability differ significantly.

Safety, Quality & Compliance (FSMA, CGMP, HACCP)
Commercial pet food in the U.S. is governed by FSMA. Similar frameworks exist in EU, Asia, and other regions. Plants must document kill-steps, traceability, and sanitation.
Checklist includes: supplier programs, kill-step validation, hygiene zoning, metal detection, and traceability.

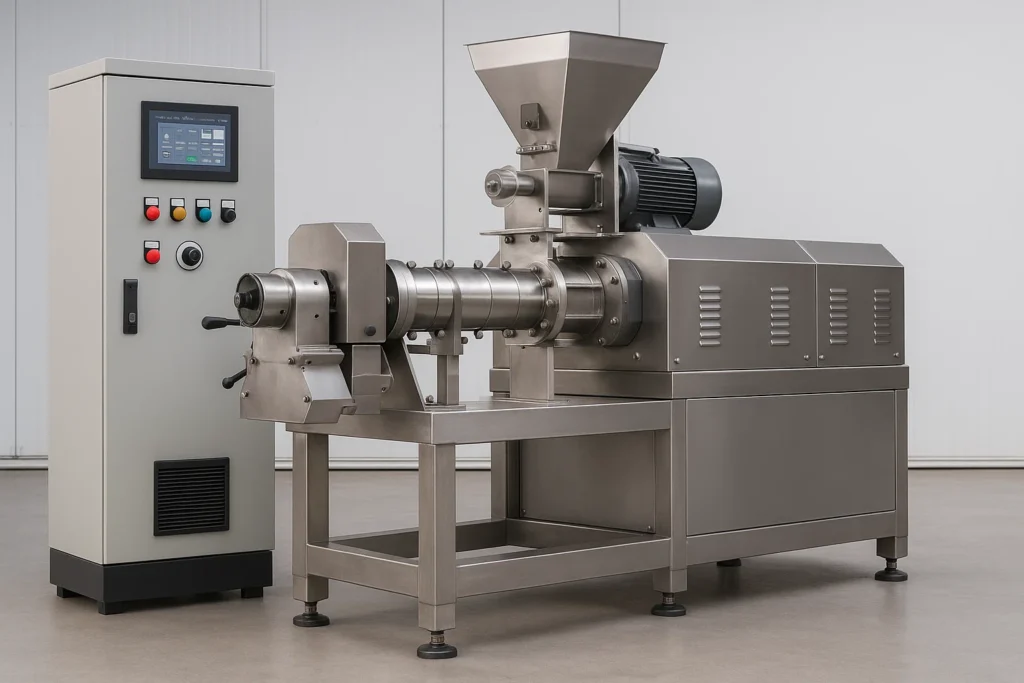
Core Equipment & Line Layout
Choosing equipment depends on product portfolio, throughput, and sanitation. A typical dry kibble layout:
Raw material intake & silos
Grinder → mixer → preconditioner
Pet Food Extruder → dryer → cooler
Coater → packaging line

Packaging Options & Shelf-Life Control
Bags (laminate): cost-effective, resealable.
Pouches: premium appeal, portion control.
Cans & retort pouches: for wet food, long shelf life.
Global Regulatory Frameworks
Different markets apply different rules:
EU (FEDIAF): requires traceability, HACCP.
China GB: strict batch documentation, bilingual labels.
Japan MAFF: strong pathogen control proof.
Middle East (Halal): halal-certified zones required.
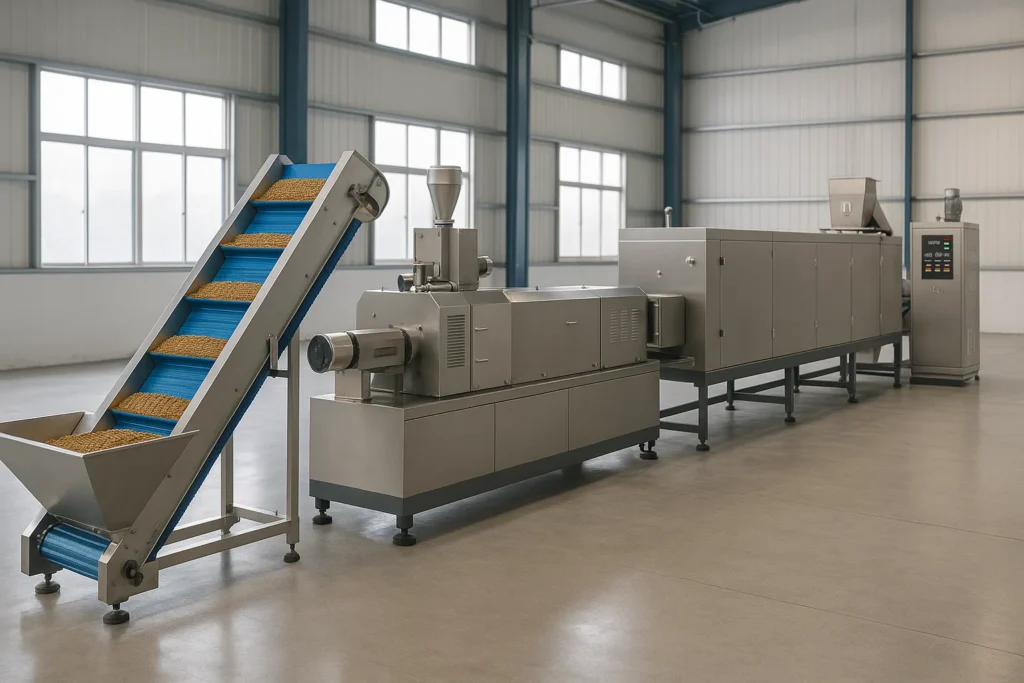

Supply Chain & Ingredient Management
Modern factories manage risks in transport and storage:
Cold chain for meats.
Grain sampling and sieving.
Oils checked for seal and quality.
Premixes verified with COAs.
Market Trends Shaping Production
Grain-free & high-meat: requires twin-screw extruders.
Freeze-dried: needs vacuum drying.
Fresh: shorter shelf life, cold-chain packaging.
Sustainable packaging: recyclable films.
Case Data & ROI
Energy savings: new dryers cut gas use by 22%.
Throughput: twin-screw raised output by 35%.
Market size: USD 160B by 2029.
Waste reduction: inline sensors cut rework 18%.
Who We Build For
We design lines for startups, growth plants, and enterprise facilities. Our Pet Food Production Line ships with FAT/SAT and training.
Common Formulation Building Blocks
- Proteins: meat meals, plant proteins.
Carbs: maize, rice,potatoes.
Fats & palatants: animal fats, omega oils.
Ready to specify equipment?
Our Pet Food Processing Equipment portfolio covers extruders, dryers, coaters, packers, with ROI benchmarks.

Q&A: Your Top Process Questions, Answered
How to size an Animal Food Processing Machine?
Start from finished goods per hour, back-calculate upstream.
What is the “kill step”?
Combination of time, temperature, pressure in extrusion.
(FAQ continues with dry vs wet, allergens, shelf life, etc.)
Which certifications matter most for EU export?
ISO 22000/FSSC 22000 and FEDIAF compliance.
How do freeze-dried lines differ from extrusion?
Freeze-dry removes water under vacuum.
Can sustainable packaging boost export sales?
Yes, especially in Europe.
Conclusion
This expanded guide has outlined not just the steps of extrusion and drying, but also supply chain, global regulations, and ROI data. For plants exploring a new Pet Food Production Line, these factors decide compliance, efficiency, and market success.